With my training nearing completion, I decided to revisit a few past problems I had failed on and find some catharsis.
Contents
- ccc2019s3 arithmetic square
- ccc2019s4 tourism
- olympiads computing competition
- codeforce1375i cubic lattice
- cco2021 day 2
- conclusion
Canadian Computing Competition 2019 S3 - Arithmetic Square
Doing well on the CCC was a big deal for me back in 2019, so I remember this problem well as my hopes of advancing to the next round were slowly destroyed over 3 long hours. I remember randomly filling in empty squares before realizing that this could lead to an inconsistent set of equations, then getting stuck on some cases with 3 elements filled in. Then Bruce showed me a clever order for filling them in that somehow magically solved it. Lets take another look at this problem…
There are definitely quite a few cases, but I don’t think any of them are that hard to solve. It would probably actually be faster to just write the code than explain everything in words. Another solution is to just write the system of equations and use elimination or something.
Canadian Computing Competition 2019 S4 - Tourism
This problem was difficult compared to previous CCC problems and also contributed to my poor performance in 2019. After upsolving this problem, I was worried about whether I would be able to solve another problem like this, and in fact even in 2020 I did not expect to solve S4 despite my improvement over the last year. Eventually some new test case got added that made almost everyone’s solution get wrong answer, so maybe the problem is even harder. We’ll see.
The first thing I noticed was there were many accepted solutions despite the extra tests. Anyway, I know my solution used monotonic dp transition or something, but can’t you just use a segment tree to find the best location to travel from? With a monostack for previous maximums of course. I’ll write a code to see if it works. And… it got AC. Nice.
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#ifndef LOCAL/*
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#pragma GCC optimize "unroll-loops"
#pragma GCC target "mmx,sse,sse2,sse3,sse4,avx,avx2,fma,abm,popcnt,tune=native" //*/
//#pragma GCC optimize "prefetch-loop-arrays"
#endif // LOCAL
using namespace std; using namespace __gnu_pbds;
#define foru(i,a,b) for(ll i=(a);i<(b);i++)
#define ford(i,a,b) for(ll i=(a)-1;i>=(b);i--)
#define fori(a,b) foru(i,a,b)
#define forj(a,b) foru(j,a,b)
#define fork(a,b) foru(k,a,b)
#define seto(x,i) memset(x,i,sizeof x)
#define pf first
#define ps second
#define pb push_back
#define eb emplace_back
#define em emplace
#define mp make_pair
#define mt make_tuple
#define popcount __builtin_popcount
#define popcountll __builtin_popcountll
#define clz __builtin_clz
#define clzll __builtin_clzll
#define ctz __builtin_ctz
#define ctzll __builtin_ctzll
#define P2(x) (1LL<<(x))
#define sz(x) (ll)x.size()
#define all(x) begin(x),end(x)
#define lwb lower_bound
#define upb upper_bound
#if __SIZEOF_INT128__
typedef __int128_t i128; typedef __uint128_t ui128;
#endif
typedef int64_t ll; typedef uint64_t ull; typedef long double lld; typedef pair<int,int> pii; typedef pair<ll,ll> pll; typedef pair<lld,lld> pdd;
template<class T1,class T2> using ordered_map=tree<T1,T2,less<T1>,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update>; template<class T1> using ordered_set=ordered_map<T1,null_type>;
template<class T> using minpq=std::priority_queue<T,vector<T>,greater<T>>; template<class T> using maxpq=std::priority_queue<T,vector<T>,less<T>>;
template<class T> using minpairingheap=__gnu_pbds::priority_queue<T,greater<T>,pairing_heap_tag>; template<class T>using maxpairingheap=__gnu_pbds::priority_queue<T,less<T>,pairing_heap_tag>;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f,MOD=1e9+7; const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; const lld PI=acos((lld)-1);
const ll SEED=443214^chrono::duration_cast<chrono::nanoseconds>(chrono::high_resolution_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count();
mt19937 randgen(SEED); ll rand(ll a, ll b){return uniform_int_distribution<ll>(a,b)(randgen);}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
ll fpow(ll a,ll b){ll ret=1;for(;b;b>>=1){if(b&1) ret=ret*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;}return ret;} ll fpow(ll a,ll b,ll M){ll ret=1;for(;b;b>>=1){if(b&1) ret=ret*a%M;a=a*a%M;}return ret;}
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr const auto _min(const T1&x,const T2&y){return x<y?x:y;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr auto _min(const T&x,const Ts&...xs){return _min(x,_min(xs...));}
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr const auto _max(const T1&x,const T2&y){return x>y?x:y;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr auto _max(const T&x,const Ts&...xs){return _max(x,_max(xs...));}
#define min(...) _min(__VA_ARGS__)
#define max(...) _max(__VA_ARGS__)
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr bool ckmin(T1&x,const T2&y){return x>y?x=y,1:0;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr bool ckmin(T&x,const Ts&...xs){return ckmin(x,min(xs...));}
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr bool ckmax(T1&x,const T2&y){return x<y?x=y,1:0;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr bool ckmax(T&x,const Ts&...xs){return ckmax(x,max(xs...));}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto operator+(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const pair<T3,T4>& b){return mp(a.pf+b.pf,a.ps+b.ps);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto operator-(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const pair<T3,T4>& b){return mp(a.pf-b.pf,a.ps-b.ps);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto operator *(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const T3& b){return mp(a.pf*b,a.ps*b);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto operator *(const T1& a,const pair<T2,T3>& b){return b*a;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto operator /(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const T3& b){return mp(a.pf/b,a.ps/b);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto& operator+=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const pair<T3,T4> &b){return a=a+b;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto& operator-=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const pair<T3,T4> &b){return a=a-b;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto& operator*=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const T3 &b){return a=a*b;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto& operator/=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const T3 &b){return a=a/b;}
template<class T,class U> void erase(T& t,const U& u){auto it=t.find(u);if(it!=end(t)) t.erase(it);}
template<class T> T pop(queue<T> &a){auto b=a.front(); a.pop(); return b;} template<class T> auto pop(T &a){auto b=a.top(); a.pop(); return b;}
template<class T> T operator -(vector<T> &a,size_t x){return a[a.size()-x];} template<class T> T operator -(deque<T> &a,size_t x){return a[a.size()-x];}
struct chash{
static ll splitmix64(ll x){x+=0x9e3779b97f4a7c15; x=(x^(x>>30))*0xbf58476d1ce4e5b9; x=(x^(x>>27))*0x94d049bb133111eb; return x^(x>>31);}
template<class T> size_t operator()(const T &x) const{return splitmix64(hash<T>()(x)+SEED);}
template<class T1,class T2> size_t operator()(const pair<T1,T2>&x)const{return 31*operator()(x.first)+operator()(x.second);}};
struct mint {//thanks benq
//static constexpr mint rt() { return RT; } // primitive root for FFT
int v; explicit operator int() const { return v; } // explicit -> don't silently convert to int
mint():v(0) {}
mint(ll _v) { v = int((-MOD < _v && _v < MOD) ? _v : _v % MOD);
if (v < 0) v += MOD; }
bool operator==(const mint& o) const {
return v == o.v; }
friend bool operator!=(const mint& a, const mint& b) {
return !(a == b); }
friend bool operator<(const mint& a, const mint& b) {
return a.v < b.v; }
//friend void re(mint& a) { ll x; re(x); a = mint(x); }
//friend string ts(mint a) { return ts(a.v); }
mint& operator+=(const mint& o) {
if ((v += o.v) >= MOD) v -= MOD;
return *this; }
mint& operator-=(const mint& o) {
if ((v -= o.v) < 0) v += MOD;
return *this; }
mint& operator*=(const mint& o) {
v = int((ll)v*o.v%MOD); return *this; }
mint& operator/=(const mint& o) { return (*this) *= inv(o); }
friend mint pow(mint a, ll p) {
mint ans = 1; assert(p >= 0);
for (; p; p /= 2, a *= a) if (p&1) ans *= a;
return ans; }
friend mint inv(const mint& a) { assert(a.v != 0);
return pow(a,MOD-2); }
mint operator-() const { return mint(-v); }
mint& operator++() { return *this += 1; }
mint& operator--() { return *this -= 1; }
friend mint operator+(mint a, const mint& b) { return a += b; }
friend mint operator-(mint a, const mint& b) { return a -= b; }
friend mint operator*(mint a, const mint& b) { return a *= b; }
friend mint operator/(mint a, const mint& b) { return a /= b; }
friend string to_string(const mint& a){ return to_string(a.v); }
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & Str, mint const & v) {
Str << v.v;
return Str;
}
friend istream& operator>> (istream& stream, mint& v){
stream>>v.v;
return stream;
}
};
void fin(string s){freopen(s.c_str(),"r",stdin);} void fout(string s){freopen(s.c_str(),"w",stdout);} void fio(string s){fin(s+".in"); fout(s+".out");}
string to_string(char c){return string(1,c);} string to_string(char* s){return (string)s;} string to_string(string s){return s;}
template<class T> string to_string(complex<T> c){stringstream ss; ss<<c; return ss.str();}
template<class T1,class T2> string to_string(pair<T1,T2> p){return "("+to_string(p.pf)+","+to_string(p.ps)+")";}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> string to_string(tuple<T1,T2,T3> p){auto [a,b,c]=p; return "("+to_string(a)+","+to_string(b)+","+to_string(c)+")";}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> string to_string(tuple<T1,T2,T3,T4> p){auto [a,b,c,d]=p; return "("+to_string(a)+","+to_string(b)+","+to_string(c)+","+to_string(d)+")";}
template<class T> string to_string(T v){string ret="{"; for(const auto& x:v) ret+=to_string(x)+","; return ret+"}";}
void DBG(){cerr<<"]"<<endl;} template<class T,class... Ts> void DBG(T x,Ts... xs){cerr<<to_string(x); if(sizeof...(xs)) cerr<<", "; DBG(xs...);}
#ifdef LOCAL
#define dbg(...) cerr<<"Line("<< __LINE__<<") -> ["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]: [", DBG(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define dbg(...) 0
#endif
#define nl "\n"
const int N=P2(20),M=0;
struct SegTree{
struct node{
ll v=-INF,lz=0;
} seg[2*N]; //replace 2*N with NN=N+(size)+10 to reduce memory
void pull(int x){
seg[x].v=max(seg[2*x].v,seg[2*x+1].v);
}
void push(int x){
if(!seg[x].lz) return;
if(x<N) fori(0,2) seg[2*x+i].lz+=seg[x].lz;
seg[x].v+=seg[x].lz;
seg[x].lz=0;
}
void build(ll *arr){
fori(0,N) seg[i+N].v=arr[i];
ford(i,N,1) pull(i);
}
void upd(int lo,int hi,ll v,int l=0,int r=N-1,int x=1){
push(x);
if(hi<l||r<lo) return;
if(lo<=l&&r<=hi){
seg[x].lz+=v; push(x);
return;
}
int mid=l+r>>1;
upd(lo,hi,v,l,mid,2*x); upd(lo,hi,v,mid+1,r,2*x+1); pull(x);
}
ll query(int lo,int hi,int l=0,int r=N-1,int x=1){
if(hi<l||r<lo) return -INF;
push(x);
if(lo<=l&&r<=hi) return seg[x].v;
int mid=l+r>>1;
return max(query(lo,hi,l,mid,2*x),query(lo,hi,mid+1,r,2*x+1));
}
} st;
ll n,K,a[N],f[N],x,y,z;
stack<pll> s;
void CHECKTHIS(){
cin>>n>>K;
fori(1,n+1){
cin>>a[i];
}
s.em(0,inf);
st.upd(0,0,INF);
fori(1,n+1){
x=i-K;
y=(i-K+K-1)/K*K;
ckmax(x,0);
assert(y<i);
while(s.top().ps<a[i]){
auto [x,y]=pop(s);
z=s.top().pf;
st.upd(z,x-1,-y);
}
z=s.top().pf;
st.upd(z,i-1,a[i]);
s.em(i,a[i]);
f[i]=st.query(x,y);
st.upd(i,i,INF+f[i]);
}
cout<<f[n]<<nl;
}
int main(){
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
#ifdef LOCAL
//fin("a.txt");
#endif
int T=1; //cin>>T;
foru(t,1,T+1){
CHECKTHIS();
}
return 0;
}
/**
*/
No need to prove anything about the transitions.
Olympiads Computing Competition
Never got around to solving this one.
- g6
- centroid
- g5
- k<=10 only
- try all 1000 max weights, for each find max vertex cover in 2^k
- g4
- this is just 2d range sum
- g3
- dp[l][r][c]=max value to convert [l,r] to c
- for interval of length x try all subintervals of length x-k+1
- g2
- need to find every prefix sum p[x], in one query you can get p[x]-p[y], you already know p[0]
- always do either (0,x) or (x,n) query
- g1
- already solved
- s6
- insert cities in increasing toll, do dsu
- try all query ends in the smaller component, check if the other end is in the other component
- why is it restricted to 5 roads per city?
Codeforces Global 9 I (1375I) - Cubic Lattice
I didn’t actually solve or even look at this problem before, but while I was testing the round I heard a lot about how impossible this problem was to solve and it seemed quite scary. I also wondered if I would ever be able to solve such a problem. Well, the problem was rated 4363r which was in my range last month for practice, so now seems like a good time.
So it’s clear that the 3 vectors need to divide each respective component of each point. If you use an algebraic structure where right angle rotation is equivalent to multiplication, such as complex numbers for 2 dimensions or quaternions for 3 dimensions, then you just need to find one number that divides all other numbers. So basically this problem is calculating GCD in quaternions. I’m not sure if the regular euclid algorithm works here, but this seems like a lot of math.
I looked at the editorial and yeah, almost all of it is trying to figure out how to do GCD on quaternions. This isn’t really a programming problem. Disappointing
Canadian Computing Olympiad Day 2
I solved none of these problems when I did the contest. But this time it wasn’t because of any stupid error, the problems were just hard. After the contest, I decided to save these problems until I got better, and hopefully I’m better now.
For each problem I have recorded my notes/thought process.
P4 - Travelling Merchant
- assume you have a strong connected component with no edges going out
- find the smallest edge from each node, that’s a lower bound
- find the node with largest lower bound in the connected component
- that’s an upper bound for the connected component
- so for that node, the upper and lower bounds equal, answer is known
- now remove the node
- so now the component will be split into several smaller components, repeat the process on the leaf component
- for each node leading into it, update its lower bound
- and update the upper bound for the remaining connected component
P5 - Weird Numeral System
- so for each distance, choose the best cutoff point
- f[x]=min cost for x..n, assume dist[1..x-1]=0
- let k be such that dep[k-1]=dep[i], dep[k]=dep[i]+1
- and k>max_child[1..i-1]
- f[i]=max_child[1..i-1]-i-(nodes i..n with a parent<i)+(k-max_child[1..i-1])+f[k]
- find max_child[1..i-1] with prefix max
- find (nodes i..n with a parent<i) with BIT
- then f[i]=A+k+f[k] for k>B
- find in O(1) using suffix max
P6 - Loop Town
- plot (i,p[i])
- each point x,y can be replaced with (x-n,y), (x,y+n)
editor’s note: split means moving a point \((x,y)\) up by \(n\), effectively “splitting” it into \((x,y+n)\) and \((x-n,y)\)
- if j<i, p[j]<p[j], and i is split, j must be split
- this greatly simplifies the structure
- can a point be split more than once?
- i’m guessing no, but the reasoning is not clear
- no - it increases inversion of everything in original block
- wait maybe?
- no - the only benefit of splitting is a subset of the original block
- wait
- NO
- ok so from here n^2 dp is already apparent, maybe need some segment tree trickery?
-
maybe not
- consider the contribution of each point splits
- all nonsplit points in the top left: -1 inversion
- all nonsplit points in the top right or bottom left: +1 inversion
- unsplit points in bottom right: impossible in optimal solution
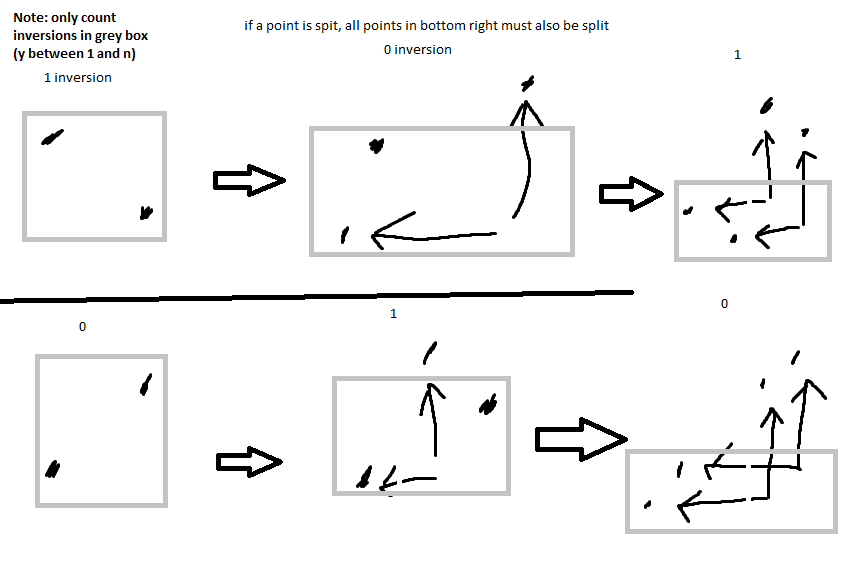
- this can be cleanly separated, in a way so you don’t care if the other points are split or not:
- in the end, subtract K(K-1) if you split K points
- +1 for everything in top right or bottom left
- -1 for everything in top left, +1 for everything in bottom right
- so two split points with this relationship will cancel out
- another +2 for everything in bottom right to compensate for subtracting K(K-1) at the end
editor note: proof/more detailed explanation
first, calculate number of initial inversions before splitting any point
a pair of points is \((p_1=(x_1,y_1), p_2=(x_2,y_2)), p_1 \neq p_2\)
let \(a\) be number of pair of points where \(p_1\) is top right or bottom left of \(p_2\), and exactly one point is split
let \(b\) be the number of pairs of points where a split \(p_1\) is to the bottom right of the unsplit \(p_2\)
then the answer is initial inversions \(+a-b\)
let \(c=\) #pairs where split \(p_1\) is bottom right of \(p_2\)
\(d=\) #pairs where split \(p_1\) is top left of \(p_2\)
\(e=\) #pairs where a split \(p_1\) is top right or bottom left of any \(p_2\)
\(f=\) #pairs where \(p_1,p_2\) are both split
remember that if \(p_1\) is split and \(p_1\) is to the top left of \(p_2\), then \(p_2\) must be also split.
\(b = c -\) #pairs where split \(p_1\) is top left of \(p_2\) (which will always also be split) \(=c-d\).
\(a= e -\) #pairs where split \(p_1\) is to the top right or bottom left of split \(p_2\)
\(=e - (\) #pairs where \(p_1,p_2\) are both split - #pairs where \(p_1,p_2\) are split and \(p_1\) is top right or bottom left of \(p_2)\)
\(=e - (f -\) #pairs where \(p_1,p_2\) are split and \(p_1\) is top right or bottom left of \(p_2)\)
\(= e-(f- 2 c)\) .
so what is needed is \(c,d,e,f\). \(f=K(K-1)\), while the contribution to \(c,d,e\) (and thus the final number of inversions) of splitting a point is independent of any other points.
- so then you can sort points by contribution and try for every K, choosing the K best points greedily
- except it’s possible for a point to be more than n higher than lower than another point
- for those points, shift x and y by a multiple of n when doing calculations
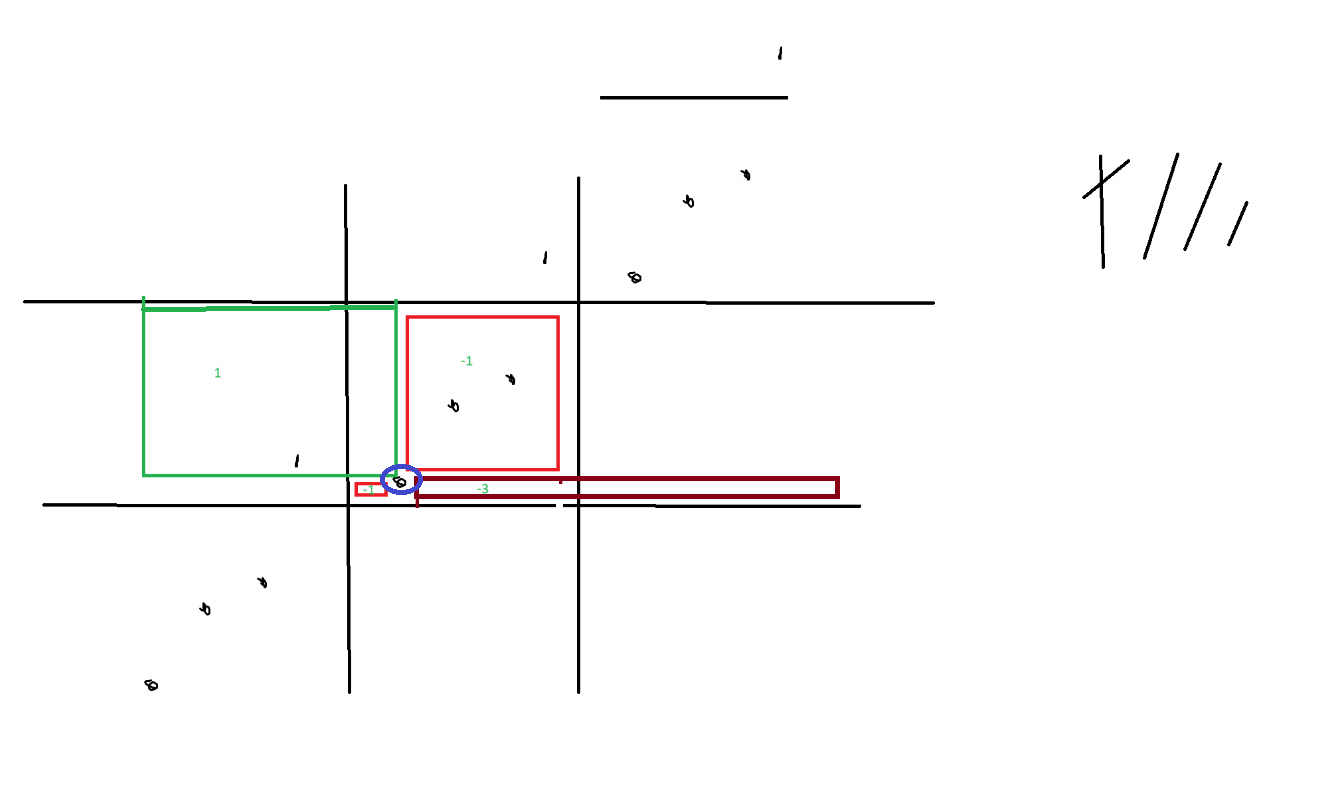 To calculate value for circled point, count the points in each box and multiply by the appropriate value for that box. Note that the green boxes extend infinitely horizontally, while the the red boxes don’t.
To calculate value for circled point, count the points in each box and multiply by the appropriate value for that box. Note that the green boxes extend infinitely horizontally, while the the red boxes don’t.
Code
Notice how the contribution of each point can be separately calculated and sorted.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#ifndef LOCAL/*
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#pragma GCC optimize "unroll-loops"
#pragma GCC target "mmx,sse,sse2,sse3,sse4,avx,avx2,fma,abm,popcnt,tune=native" //*/
//#pragma GCC optimize "prefetch-loop-arrays"
#endif // LOCAL
using namespace std; using namespace __gnu_pbds;
#define foru(i,a,b) for(ll i=(a);i<(b);i++)
#define ford(i,a,b) for(ll i=(a)-1;i>=(b);i--)
#define fori(a,b) foru(i,a,b)
#define forj(a,b) foru(j,a,b)
#define fork(a,b) foru(k,a,b)
#define seto(x,i) memset(x,i,sizeof x)
#define pf first
#define ps second
#define pb push_back
#define eb emplace_back
#define em emplace
#define mp make_pair
#define mt make_tuple
#define popcount __builtin_popcount
#define popcountll __builtin_popcountll
#define clz __builtin_clz
#define clzll __builtin_clzll
#define ctz __builtin_ctz
#define ctzll __builtin_ctzll
#define P2(x) (1LL<<(x))
#define sz(x) (ll)x.size()
#define all(x) begin(x),end(x)
#define lwb lower_bound
#define upb upper_bound
#if __SIZEOF_INT128__
typedef __int128_t i128; typedef __uint128_t ui128;
#endif
typedef int64_t ll; typedef uint64_t ull; typedef long double lld; typedef pair<int,int> pii; typedef pair<ll,ll> pll; typedef pair<lld,lld> pdd;
template<class T1,class T2> using ordered_map=tree<T1,T2,less<T1>,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update>; template<class T1> using ordered_set=ordered_map<T1,null_type>;
template<class T> using minpq=std::priority_queue<T,vector<T>,greater<T>>; template<class T> using maxpq=std::priority_queue<T,vector<T>,less<T>>;
template<class T> using minpairingheap=__gnu_pbds::priority_queue<T,greater<T>,pairing_heap_tag>; template<class T>using maxpairingheap=__gnu_pbds::priority_queue<T,less<T>,pairing_heap_tag>;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f,MOD=1e9+7; const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; const lld PI=acos((lld)-1);
const ll SEED=443214^chrono::duration_cast<chrono::nanoseconds>(chrono::high_resolution_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count();
mt19937 randgen(SEED); ll rand(ll a, ll b){return uniform_int_distribution<ll>(a,b)(randgen);}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
ll fpow(ll a,ll b){ll ret=1;for(;b;b>>=1){if(b&1) ret=ret*a%MOD;a=a*a%MOD;}return ret;} ll fpow(ll a,ll b,ll M){ll ret=1;for(;b;b>>=1){if(b&1) ret=ret*a%M;a=a*a%M;}return ret;}
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr const auto _min(const T1&x,const T2&y){return x<y?x:y;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr auto _min(const T&x,const Ts&...xs){return _min(x,_min(xs...));}
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr const auto _max(const T1&x,const T2&y){return x>y?x:y;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr auto _max(const T&x,const Ts&...xs){return _max(x,_max(xs...));}
#define min(...) _min(__VA_ARGS__)
#define max(...) _max(__VA_ARGS__)
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr bool ckmin(T1&x,const T2&y){return x>y?x=y,1:0;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr bool ckmin(T&x,const Ts&...xs){return ckmin(x,min(xs...));}
template<class T1,class T2>constexpr bool ckmax(T1&x,const T2&y){return x<y?x=y,1:0;} template<class T,class...Ts>constexpr bool ckmax(T&x,const Ts&...xs){return ckmax(x,max(xs...));}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto operator+(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const pair<T3,T4>& b){return mp(a.pf+b.pf,a.ps+b.ps);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto operator-(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const pair<T3,T4>& b){return mp(a.pf-b.pf,a.ps-b.ps);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto operator *(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const T3& b){return mp(a.pf*b,a.ps*b);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto operator *(const T1& a,const pair<T2,T3>& b){return b*a;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto operator /(const pair<T1,T2>& a,const T3& b){return mp(a.pf/b,a.ps/b);}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto& operator+=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const pair<T3,T4> &b){return a=a+b;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> constexpr const auto& operator-=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const pair<T3,T4> &b){return a=a-b;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto& operator*=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const T3 &b){return a=a*b;}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> constexpr const auto& operator/=(pair<T1,T2> &a,const T3 &b){return a=a/b;}
template<class T,class U> void erase(T& t,const U& u){auto it=t.find(u);if(it!=end(t)) t.erase(it);}
template<class T> T pop(queue<T> &a){auto b=a.front(); a.pop(); return b;} template<class T> auto pop(T &a){auto b=a.top(); a.pop(); return b;}
template<class T> T operator -(vector<T> &a,size_t x){return a[a.size()-x];} template<class T> T operator -(deque<T> &a,size_t x){return a[a.size()-x];}
struct chash{
static ll splitmix64(ll x){x+=0x9e3779b97f4a7c15; x=(x^(x>>30))*0xbf58476d1ce4e5b9; x=(x^(x>>27))*0x94d049bb133111eb; return x^(x>>31);}
template<class T> size_t operator()(const T &x) const{return splitmix64(hash<T>()(x)+SEED);}
template<class T1,class T2> size_t operator()(const pair<T1,T2>&x)const{return 31*operator()(x.first)+operator()(x.second);}};
struct mint {//thanks benq
//static constexpr mint rt() { return RT; } // primitive root for FFT
int v; explicit operator int() const { return v; } // explicit -> don't silently convert to int
mint():v(0) {}
mint(ll _v) { v = int((-MOD < _v && _v < MOD) ? _v : _v % MOD);
if (v < 0) v += MOD; }
bool operator==(const mint& o) const {
return v == o.v; }
friend bool operator!=(const mint& a, const mint& b) {
return !(a == b); }
friend bool operator<(const mint& a, const mint& b) {
return a.v < b.v; }
//friend void re(mint& a) { ll x; re(x); a = mint(x); }
//friend string ts(mint a) { return ts(a.v); }
mint& operator+=(const mint& o) {
if ((v += o.v) >= MOD) v -= MOD;
return *this; }
mint& operator-=(const mint& o) {
if ((v -= o.v) < 0) v += MOD;
return *this; }
mint& operator*=(const mint& o) {
v = int((ll)v*o.v%MOD); return *this; }
mint& operator/=(const mint& o) { return (*this) *= inv(o); }
friend mint pow(mint a, ll p) {
mint ans = 1; assert(p >= 0);
for (; p; p /= 2, a *= a) if (p&1) ans *= a;
return ans; }
friend mint inv(const mint& a) { assert(a.v != 0);
return pow(a,MOD-2); }
mint operator-() const { return mint(-v); }
mint& operator++() { return *this += 1; }
mint& operator--() { return *this -= 1; }
friend mint operator+(mint a, const mint& b) { return a += b; }
friend mint operator-(mint a, const mint& b) { return a -= b; }
friend mint operator*(mint a, const mint& b) { return a *= b; }
friend mint operator/(mint a, const mint& b) { return a /= b; }
friend string to_string(const mint& a){ return to_string(a.v); }
friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & Str, mint const & v) {
Str << v.v;
return Str;
}
friend istream& operator>> (istream& stream, mint& v){
stream>>v.v;
return stream;
}
};
void fin(string s){freopen(s.c_str(),"r",stdin);} void fout(string s){freopen(s.c_str(),"w",stdout);} void fio(string s){fin(s+".in"); fout(s+".out");}
string to_string(char c){return string(1,c);} string to_string(char* s){return (string)s;} string to_string(string s){return s;}
template<class T> string to_string(complex<T> c){stringstream ss; ss<<c; return ss.str();}
template<class T1,class T2> string to_string(pair<T1,T2> p){return "("+to_string(p.pf)+","+to_string(p.ps)+")";}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3> string to_string(tuple<T1,T2,T3> p){auto [a,b,c]=p; return "("+to_string(a)+","+to_string(b)+","+to_string(c)+")";}
template<class T1,class T2,class T3,class T4> string to_string(tuple<T1,T2,T3,T4> p){auto [a,b,c,d]=p; return "("+to_string(a)+","+to_string(b)+","+to_string(c)+","+to_string(d)+")";}
template<class T> string to_string(T v){string ret="{"; for(const auto& x:v) ret+=to_string(x)+","; return ret+"}";}
void DBG(){cerr<<"]"<<endl;} template<class T,class... Ts> void DBG(T x,Ts... xs){cerr<<to_string(x); if(sizeof...(xs)) cerr<<", "; DBG(xs...);}
#ifdef LOCAL
#define dbg(...) cerr<<"Line("<< __LINE__<<") -> ["<<#__VA_ARGS__<<"]: [", DBG(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define dbg(...) 0
#endif
#define nl "\n"
const int N=2e6+10,M=0;
struct BITree{
ll bit[N];
void upd(int x,int v){
for(ckmin(++x,N);x<N;x+=x&-x) bit[x]+=v;
}
ll query(int x){
ll ret=0;
if(x<0){
return 0;
}
for(ckmin(++x,N-1);x;x-=x&-x) ret+=bit[x];
return ret;
}
ll query(int l,int r){
return query(r)-query(l-1);
}
} b1,b2;
ll n,aa[N],ab[N],p[N],v1[N],v2[N],v3[N],v4[N],v5[N],val[N],ans,t,t2;
vector<ll> xs,ys;
void input(){
cin>>n>>t;
fori(0,n){
cin>>aa[i]>>ab[i];
}
}
void solve(){
input();
fori(0,n){
xs.pb(aa[i]); ys.pb(ab[i]);
}
sort(all(xs)); sort(all(ys));
fori(0,n){
p[lwb(all(xs),aa[i])-begin(xs)]=lwb(all(ys),ab[i])-begin(ys);
}
fori(0,n){
if(p[i]<i){
p[i]+=n;
}
}
fori(0,n){
v1[i]=b1.query(p[i]-n,p[i]);
v2[i]+=b1.query(p[i],inf);
v3[i]+=b1.query(-inf,p[i]-n);
b1.upd(p[i],1);
t2+=i-v1[i]; //guilty or innocent?
}
ford(i,n,0){
v2[i]+=b2.query(p[i]+n,inf);
v3[i]+=b2.query(p[i]);//same as p[i]-n,p[i]
v4[i]=b2.query(p[i],p[i]+n);
b2.upd(p[i],1);
}
fori(0,n){
val[i]=v2[i]-v1[i]-v4[i]-v3[i]*3;
}
sort(val,val+n); reverse(val,val+n);
t=0;
fori(0,n){
t+=val[i];
ckmax(ans,t+i*(i+1));
}
ans=-ans;
ans+=t2;
cout<<ans<<nl;
}
int main(){
cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(0);
#ifdef LOCAL
fin("a.txt");
#endif
int T=1; //cin>>T;
foru(t,1,T+1){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
/**
*/
Conclusion
From the results of the contest and mirror, the ratings for P4, P5, P6 are estimated at 2600r, 2500r, 4200r respectively. That feels about right. Looking back, I think I might have solved p4 or p5 during the contest back in 2021 if I spent more time on one of them and kept calm, but I definitely had no chance with p6. All problems were pretty good and interesting. Looking at the official editorials, my solution for p4 and p5 were intended, but my p6 solution was unlike any other submission on dmoj or ojuz. Speaking of loops, this is a very good song.
Overall, this was a fun activity and it feels good to finally solve or resolve these problems from scratch.